session
Cache and restore cookies,
localStorage,
and
sessionStorage
in order to reduce test setup times.
Experimental
The session API is currently experimental, and can be enabled by setting the
experimentalSessionAndOrigin option to
true in the Cypress config.
Enabling this flag does the following:
- It adds the
cy.session()andcy.origin()commands, andCypress.sessionAPI. - It adds the following new behaviors (that will be the default in a future
major update of Cypress) at the beginning of each test:
- The page is cleared (by setting it to
about:blank). Disable this by settingtestIsolation=legacy. - All active session data (cookies,
localStorageandsessionStorage) across all domains are cleared.
- The page is cleared (by setting it to
- It overrides the
Cypress.Cookies.preserveOnce()andCypress.Cookies.defaults()methods. - Cross-origin navigation will no longer fail immediately, but instead, time out
based on
pageLoadTimeout. - Tests will no longer wait on page loads before moving on to the next test.
Because the page is cleared at the beginning of each test,
cy.visit() must be explicitly called at the beginning
of each test.
Syntax
cy.session(id, setup)
cy.session(id, setup, options)
Usage
Correct Usage
// Caching session when logging in via API
cy.session(username, () => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: '/login',
body: { username, password },
}).then(({ body }) => {
window.localStorage.setItem('authToken', body.token)
})
})
// Caching session when logging in via page visit
cy.session(name, () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type('s3cr3t')
cy.get('form').contains('Log In').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/login-successful')
})
Incorrect Usage
// visiting before calling cy.session() is redundant, it needs to
// be done inside the setup function
cy.visit('/login')
cy.session(name, () => {
// need to call cy.visit() here because the page is blank when
// the setup function runs
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type('s3cr3t')
cy.get('form').contains('Log In').click()
// should assert that login was successful here to guarantee the
// login process completes before it is cached
})
// should have asserted this inside the cy.session() setup
// function because the page is blank here
cy.url().should('contain', '/login-successful')
Arguments
id (String, Array, Object)
A unique identifier that will be used to cache and restore a given session. In
simple cases, a String value is sufficient. In order to simplify generation of
more complex ids, if you pass an Array or Object, Cypress will generate an
id for you by deterministically stringifying the value you pass in. For example,
if you pass ['Jane', '123', 'admin'], an id of ["Jane","123","admin"] will
be generated for you.
See the choosing the correct id to cache a session section for a more thorough explanation with examples.
Note that large or cyclical data structures may be slow or difficult to serialize into an identifier, so exercise care with the data you specify.
setup (Function)
This function is called whenever a session for the given id hasn't yet been
cached, or if it's no longer valid (see the validate option). After setup
runs, Cypress will preserve all cookies, sessionStorage, and localStorage,
so that subsequent calls to cy.session() with the same id will bypass
setup and just restore the cached session data.
The page and all active session data (cookies, localStorage and
sessionStorage) across all domains are always cleared before setup runs.
options (Object)
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
validate | undefined | Validates the newly-created or restored session. Function to run immediately after the session is created and setup function runs or after a session is restored and the page is cleared. If this returns false, throws an exception, contains any failing Cypress command, or returns a Promise which rejects or resolves to false, the session is considered invalid.- If validation fails immediately after setup, the test will fail.- If validation fails after restoring a session, setup will re-run. |
cacheAcrossSpecs | false | When enabled, the newly created session is considered "global" and can be restored in any spec during the test execution in the same Cypress run on the same machine. Use this option for a session that will be used multiple times, across many specs. |
Yields
cy.session()yieldsnull.
Examples
Updating an existing login custom command
You can add session caching to your login
custom command. Wrap the inside of the
command with a call to cy.session().
Before
Cypress.Commands.add('login', (username, password) => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: '/login',
body: { username, password },
}).then(({ body }) => {
window.localStorage.setItem('authToken', body.token)
})
})
After
Cypress.Commands.add('login', (username, password) => {
cy.session([username, password], () => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: '/login',
body: { username, password },
}).then(({ body }) => {
window.localStorage.setItem('authToken', body.token)
})
})
})
With session validation
Cypress.Commands.add('login', (username, password) => {
cy.session(
[username, password],
() => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: '/login',
body: { username, password },
}).then(({ body }) => {
window.localStorage.setItem('authToken', body.token)
})
},
{
validate() {
cy.request('/whoami').its('status').should('eq', 200)
},
}
)
})
Updating an existing login helper function
You can add session caching to a login helper function by wrapping the inside of
the function with a call to cy.session().
Before
const login = (name, password) => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type(password)
cy.get('#submit').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/home')
}
After
const login = (name, password) => {
cy.session([name, password], () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type(password)
cy.get('#submit').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/home')
})
}
With session validation
const login = (name, password) => {
cy.session(
[name, password],
() => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type(password)
cy.get('#submit').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/home')
},
{
validate() {
cy.visit('/account-details')
},
}
)
}
Asserting the session inside setup
Because cy.session() caches session data immediately after the setup
function completes, it's a best practice to assert that the login process has
completed at the end of session setup, to ensure that setup doesn't return
before the session data is available to be cached.
Asserting sessions in this way can help simplify your login custom command, and reduce the need to conditionally cache sessions.
cy.session('user', () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type('p4ssw0rd123')
cy.get('#login').click()
// Wait for the post-login redirect to ensure that the
// session actually exists to be cached
cy.url().should('contain', '/login-successful')
})
Conditionally caching a session
Specs usually contain two types of tests where logins are necessary:
- Testing functionality that only exists for logged-in users
- Testing the act of logging in
For the first, caching sessions can be incredibly useful for reducing the amount of time it takes to run tests. However, for the second, it may be necessary to not cache the session, so that other things can be asserted about the login process.
In this case, it can be helpful to create a custom login command that will conditionally cache the session. However, wherever possible, it's better to assert the session inside setup.
Cypress.Commands.add('login', (name, { cacheSession = true } = {}) => {
const login = () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type('p4ssw0rd123')
cy.get('#login').click()
}
if (cacheSession) {
cy.session(name, login)
} else {
login()
}
})
// Testing the login flow itself
describe('login', () => {
it('should redirect to the correct page after logging in', () => {
cy.login('user', { cacheSession: false })
cy.url().should('contain', '/login-successful')
})
})
// Testing something that simply requires being logged in
describe('account details', () => {
it('should have the correct document title', () => {
cy.login('user')
cy.visit('/account')
cy.title().should('eq', 'User Account Details')
})
})
Switching sessions inside tests
Because cy.session() clears the page and all active session data before
running setup, you can use it to easily switch between sessions without first
needing to log the previous user out. This allows tests to more accurately
represent real-world scenarios and helps keep test run times short.
const login = (name) => {
cy.session(name, () => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: '/login',
body: { name, password: 's3cr3t' },
}).then(({ body }) => {
window.localStorage.setItem('authToken', body.token)
})
})
}
it('should transfer money between users', () => {
login('user')
cy.visit('/transfer')
cy.get('#amount').type('100.00')
cy.get('#send-money').click()
login('other-user')
cy.visit('/account_balance')
cy.get('#balance').should('eq', '100.00')
})
Validating the session
If the validate function return false, throws an exception, returns a
Promise that resolves to false or rejects, or contains any failing Cypress
command, the session will be considered invalid, and setup will be re-run.
The page is not cleared after the validate function is executed. If you use
cy.visit() in your validation, your test will continue on the visited page
once cy.session() succeeds.
Here are a few validate examples:
// Attempt to visit a page that only a logged-in user can see
function validate() {
cy.visit('/private')
}
// Make an API request that returns a 200 only when logged in
function validate() {
cy.request('/api/user').its('status').should('eq', 200)
}
// Run any Cypress command that fails if the user is not logged in
function validate() {
cy.visit('/account', { failOnStatusCode: false })
cy.url().should('match', /^/account/)
}
// Or just return false if the session is invalid
function validate() {
if (!MyApp.isSessionValid()) {
return false
}
}
Modifying session data before caching
If you want to change which session data is cached, you can modify cookies,
localStorage, sessionStorage as-necessary in setup.
cy.session('user', () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('name').type('user')
cy.get('password').type('p4ssw0rd123')
cy.get('#submit').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/home')
// Remove session data we don't want to cache
cy.clearCookie('authId')
cy.window().then((win) => {
win.localStorage.removeItem('authToken')
})
// Add session data we do want to cache
cy.setCookie('session_id', '189jd09sufh33aaiidhf99d09')
})
Caching session data across specs
If you want to use the same session across multiple specs in the same Cypress
run on the same machine, add cacheAcrossSpecs=true to the session options to
leverage the session through the run.
const login = (name = 'user1') => {
cy.session(name, () => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: '/login',
body: { name, password: 's3cr3t' },
}).then(({ body }) => {
window.localStorage.setItem('authToken', body.token)
})
}, {
validate() {
cy.visit('/user_profile')
cy.contains(`Hello ${name}`)
}
cacheAcrossSpecs: true,
})
}
// profile.cy.js
it('can view profile', () => {
cy.login()
})
// add_blog.cy.js
it('can create a blog post', () => {
cy.login()
})
Multiple login commands
A more complex app may require multiple login commands, which may require
multiple uses of cy.session(). However, because the id value is used as a
unique identifier to save and restore sessions, it's very important that it's
actually unique per session.
In the following example, if the resulting session data that loginByForm and
loginByApi create is different in any way, it would be a mistake to specify
[name, password] as the id for both, because there would be no way to
distinguish between the sessions created by loginByForm("user", "p4ssw0rd")
and loginByApi("user", "p4ssw0rd"). Instead, you can modify the id to
differentiate its value between both login functions, so that each will always
be cached uniquely.
const loginByForm = (name, password) => {
cy.session(['loginByForm', name], () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type(password)
cy.get('#submit').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/home')
})
}
const loginByApi = (name, password) => {
cy.session(['loginByApi', name], () => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: '/api/login',
body: { name, password },
}).then(({ body }) => {
window.localStorage.setItem('authToken', body.token)
})
})
}
Where to call cy.visit()
If you call cy.visit() immediately after cy.session()
in your login function or custom command, it will effectively behave the same as
a login function without any session caching.
const login = (name) => {
cy.session(name, () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type('s3cr3t')
cy.get('#submit').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/home')
})
cy.visit('/home')
}
beforeEach(() => {
login('user')
})
it('should test something on the /home page', () => {
// assertions
})
it('should test something else on the /home page', () => {
// assertions
})
However, any time you want to test something on a different page, you will need
to call cy.visit() at the beginning of that test, which will then be
effectively calling cy.visit() twice in a row, which will result in slightly
slower tests.
// ...continued...
it('should test something on the /other page', () => {
cy.visit('/other')
// assertions
})
Tests will often be faster if you call cy.visit() only when necessary. This
works especially well when
organizing tests into suites
and calling cy.visit() after logging in inside a
beforeEach hook.
const login = (name) => {
cy.session(name, () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type('s3cr3t')
cy.get('#submit').click()
cy.url().should('contain', '/home')
})
// no visit here
}
describe('home page tests', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
login('user')
cy.visit('/home')
})
it('should test something on the /home page', () => {
// assertions
})
it('should test something else on the /home page', () => {
// assertions
})
})
describe('other page tests', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
login('user')
cy.visit('/other')
})
it('should test something on the /other page', () => {
// assertions
})
})
Updating a login function that returns a value
If your custom login command returns a value that you use to assert in a test,
wrapping it with cy.session() will break that test. However, it's usually easy
to solve this by refactoring the login code to assert directly inside setup.
Before
Cypress.Commands.add('loginByApi', (username, password) => {
return cy.request('POST', `/api/login`, {
username,
password,
})
})
it('should return the correct value', () => {
cy.loginByApi('user', 's3cr3t').then((response) => {
expect(response.status).to.eq(200)
})
})
After
Cypress.Commands.add('loginByApi', (username, password) => {
cy.session(username, () => {
cy.request('POST', `/api/login`, {
username,
password,
}).then((response) => {
expect(response.status).to.eq(200)
})
})
})
it('is a redundant test', () => {
/* which you can now delete! */
})
Cross-domain sessions
It's possible to switch domains while caching sessions, just be sure to
explicitly visit the domain in your login command before calling cy.session().
const login = (name) => {
if (location.hostname !== 'example.com') {
cy.visit('example.com')
}
cy.session(name, () => {
cy.visit('/login')
// etc
}, {
validate() {
cy.request('/whoami', {
headers: { 'Authorization' : localStorage.token }
method: 'POST'
}).its('status').should('equal', 200)
}
})
}
it('t1', () => {
login('bob')
// do things on example.com
})
it('t2', () => {
cy.visit('anotherexample.com')
// do things on anotherexample.com
})
it('t3', () => {
login('bob')
// do things on example.com
})
Notes
When the page and active session data are cleared
The page is cleared and all active session data (cookies, localStorage, and
sessionStorage) across all domains are cleared automatically when
cy.session() runs. This guarantees consistent behavior whether a session is
being created or restored and allows you to switch sessions without first having
to explicitly log out.
| Current page cleared | Active session data cleared | |
|---|---|---|
Before setup | ||
Before validate | ||
After cy.session() |
Calling cy.session() clears the current page in addition to restoring the
cached session data. cy.visit() must be explicitly
called afterwards to ensure a page is visited if you did not provide a
validate function that called cy.visit().
Session caching
Once created, a session for a given id is cached for the duration of the spec
file. You can't modify a stored session after it has been cached, but you can
always create a new session with a different id.
In order to reduce development time, when running Cypress in "open" mode, sessions will be cached for spec file reruns.
To persist a session across multiple specs, use the option
cacheAcrossSpecs=true.
Explicitly clearing sessions
When running Cypress in "open" mode, you can explicitly clear all spec and global sessions and re-run the spec file by clicking the "Clear All Sessions" button in the Instrument Panel.
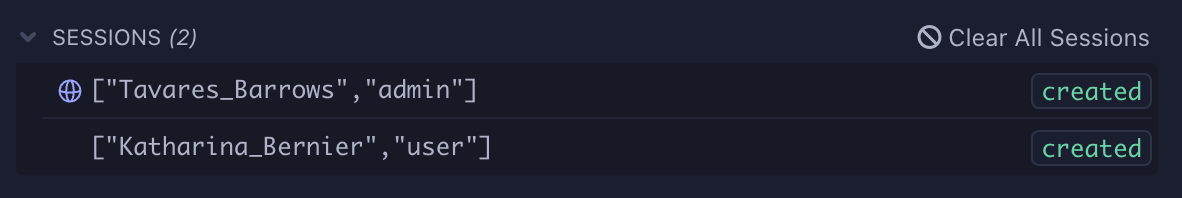
For debugging purposes, all spec and global sessions can be cleared with the
Cypress.session.clearAllSavedSessions() method.
Where to call cy.session()
While it is possible to call cy.session() explicitly inside a test or
beforeEach, it is considered a best practice to call cy.session() inside a
login custom command or reusable wrapper
function. See the
Updating an existing login custom command
and
Updating an existing login helper function
examples for more details.
Choosing the correct id to cache a session
In order for sessions to be cached uniquely, the id argument
must be unique for each new session created. The id provided to cy.session()
will display in the reporter, thus we do not recommend using sensitive data like
passwords or tokens as unique identifiers.
// If your session setup code uses a string variable, pass in the
// string as the id
const login = (name) => {
cy.session(name, () => {
loginWith(name)
})
}
// If your session setup code uses a single object, pass in the
// object as the id and it will be serialized into an identifier
const login = (params = {}) => {
cy.session(params, () => {
loginWith(params)
})
}
// If your session setup code uses multiple variables, pass in an
// array of those variables and it will be serialized into an
// identifier
const login = (name, email, params = {}) => {
cy.session([name, email, params], () => {
loginWith(name, email, params)
})
}
// If your session setup code uses external constants, they don't
// need to be included in the id, since they will never change
const API_KEY = 'I_AM_AN_API_KEY'
const login = (name, email) => {
cy.session([name, email], () => {
loginWith(name, email, API_KEY)
})
}
Incorrect Usage
If you have custom login code that uses multiple parameters (in this example,
a name, a token, and a password), in order to be able to log in many different
users, but the id only included one of them (in this example, name):
const login = (name, token, password) => {
cy.session(name, () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=token]').type(token)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type(password)
cy.get('#submit').click()
})
}
If you ran this, user1 would be logged in with token1 and p4ssw0rd, and a
session would be created and cached using "user1" as the id.
login('user1', 'token1', 'p4ssw0rd')
Now let's say you wanted to try to log in the same user, but with a different
token and/or password, and expect a different session to be created and cached.
You run this, but because cy.session() is only being passed name as its
id, it won't create a new session, but will instead load the saved session for
"user1".
login('user1', 'different-token', 'p4ssw0rd')
In summary, you need to ensure that the id is unique. Create it from all the
parameters used inside the setup function that may change, otherwise id
values may collide and create unexpected results.
Correct Usage
In this example, setting the id to [name, uniqueKey] guarantees that calling
login() with different name, token and password values will create and
cache unique sessions.
const login = (name, token, password, uniqueKey) => {
cy.session([name, uniqueKey], () => {
cy.visit('/login')
cy.get('[data-test=name]').type(name)
cy.get('[data-test=token]').type(token)
cy.get('[data-test=password]').type(password)
cy.get('#submit').click()
})
}
The uuid npm package can be used to
generate random unique ids if an arbitrary name-space does not meet your needs.
Common Questions
Why are all my Cypress commands failing after calling cy.session()?
Ensure that you're calling cy.visit() after calling
cy.session(), otherwise your tests will be running on a blank page.
Why am I seeing 401 errors after calling cy.session()?
It's possible that your session has been invalidated. Be sure to specify a
validate function so that cy.session() can validate and recreate the session
if necessary.
Command Log
The Instrument Panel
Whenever a session is created or restored inside a test, an extra instrument panel is displayed at the top of the test to give more information about the state of your sessions.
Clicking any session id in the panel will print that session's details to the
console, and clicking the "Clear All Sessions" button will clear all saved spec
and global sessions and re-run the spec file (see
Session caching for more details).

The command log
Whenever cy.session() is called, the command log will show one of the
following lines, which includes the status of the session call along with the
session id value:
-
No saved session was found, so a new session was created and saved:

-
A saved session was found, and used:

-
A saved session was found, but the
validatefunction failed, so the session was recreated and saved:
Note that in cases where the validate function fails immediately after setup
creates the session, the test will fail with an error.
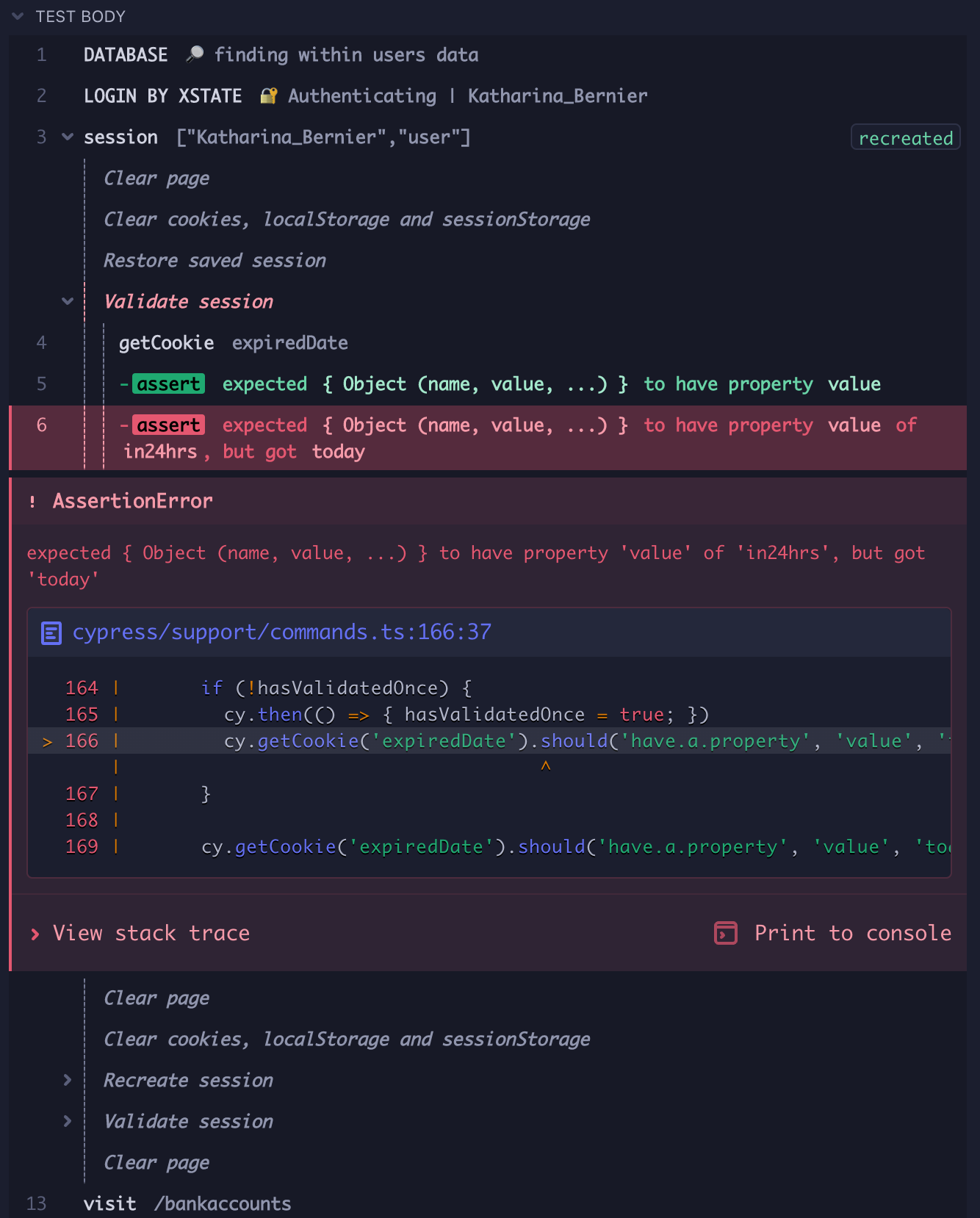
Expanding the session group in the command log will show all of the commands that were run when creating and/or validating the session.
In this image, a saved session is restored, but when /personal is visited in
the validate function, the app redirects to /signin, which invalidates the
session. A new session is created by visiting /signin where the user is logged
in, after which, validation succeeds, and the session is made active for the
remainder of the test.
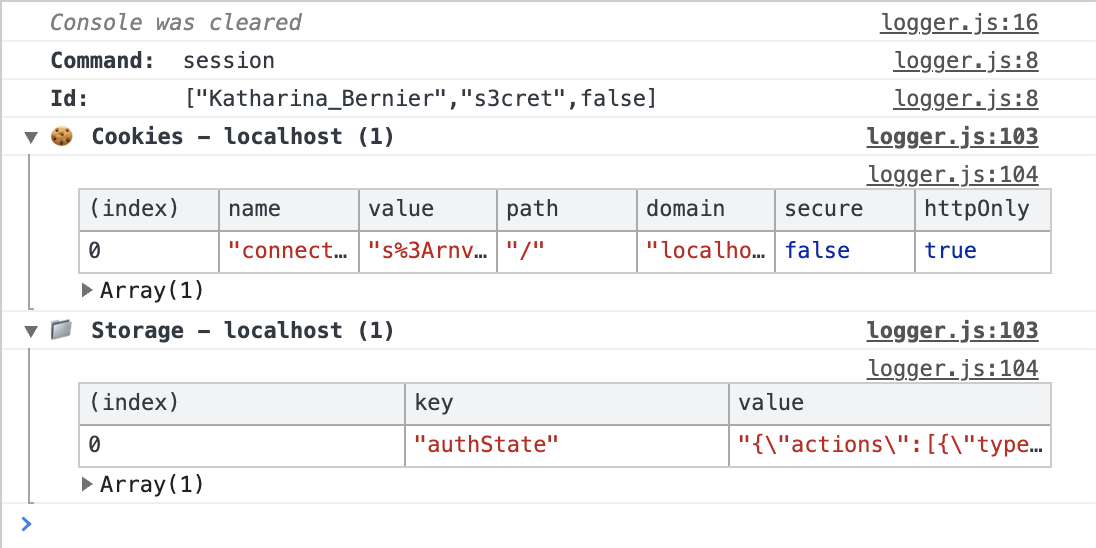
Printing to the console
Clicking a session id in the Instrument Panel or clicking the first line under
an expanded session group in the command log will print that session's details
to the console. This information contains the id along with any cached session
data, including cookies, localStorage and sessionStorage.